Since the ketogenic diet was developed in the 1920’s, several variations have emerged, including the modified Atkins diet, also called “MAD”. If you are considering the medical ketogenic diet for the dietary management of drug-resistant epilepsy (also referred to as: intractable or refractory epilepsy) for your child or yourself, you may have come across the “modified Atkins diet” and wondered what it is and how it’s different from the classic ketogenic diet.
Differences Between the Modified Atkins Diet and the Classic Ketogenic Diet
- Unrestricted Protein
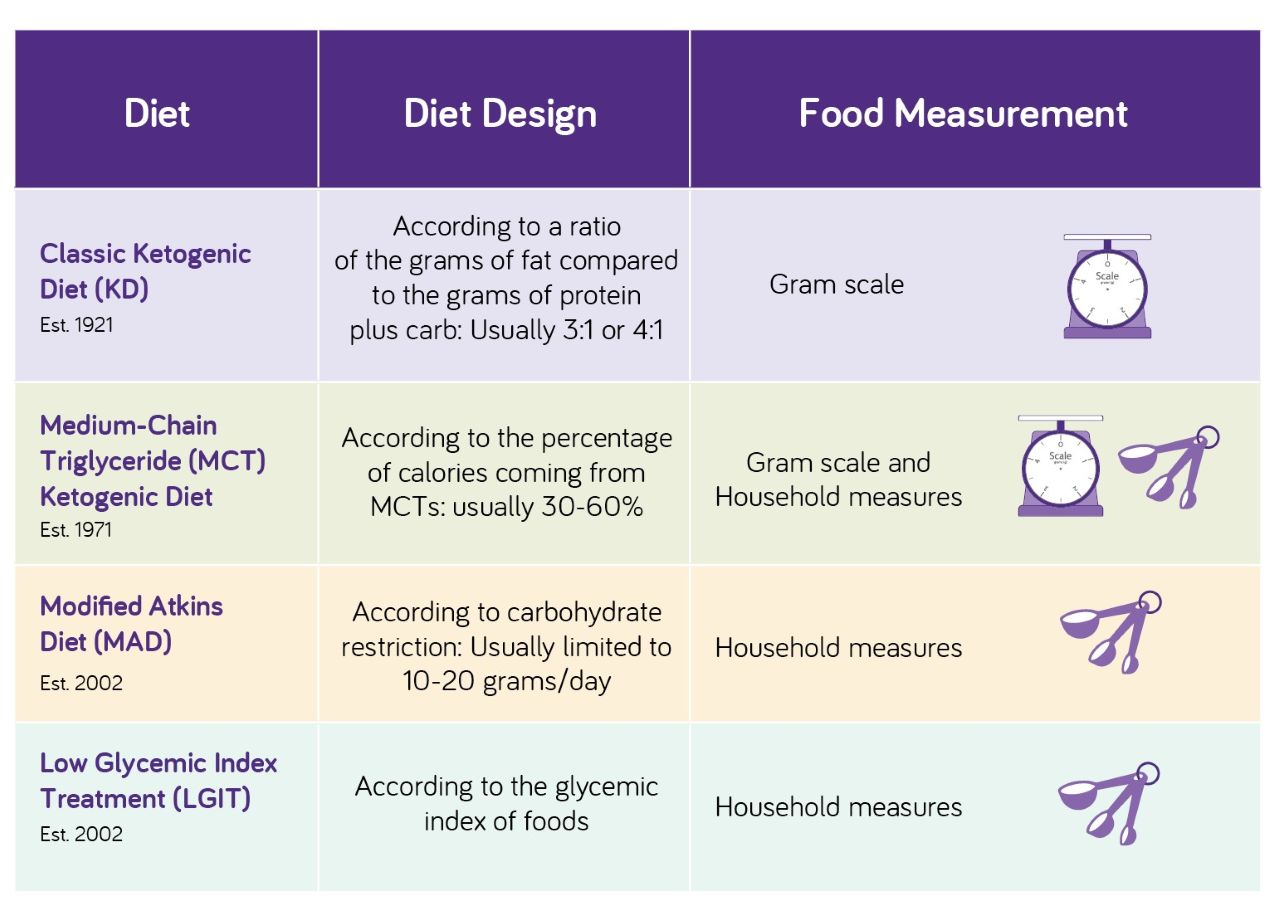
The classic ketogenic diet is designed to provide “adequate protein”, meaning that patients eat enough to sustain their body mass, but no extra. The modified Atkins diet does not restrict the amount of protein in the diet. - Food Measurement
While the classic ketogenic diet requires that foods be weighed on a gram scale, foods are measured using household measurements (like cups, tablespoons, etc.) on the modified Atkins diet. - Ratio of Fat to Carbohydrate & Protein
The classic ketogenic diet is designed according to a ratio, usually 4:1 or 3:1 (grams of fat: carbohydrate + protein). The modified Atkins diet is not designed according to a ratio, but is simply based on limiting net carbohydrates, usually to 10-20 grams/day. - Diet Initiation
While hospital admission is usually required when starting the classic ketogenic diet, the modified Atkins diet is initiated at home.
Similarities Between the Modified Atkins Diet and the Classic Ketogenic Diet
- Restricted Carbohydrates
Like the Classic Ketogenic Diet, carbohydrates are restricted on the modified Atkins diet. Hidden sources of carbohydrate must still be monitored to ensure that patients are not consuming more than the recommended amount. Label reading is a must for all over-the-counter products as well. - Fat Consumption
Fat consumption is encouraged on the modified Atkins diet. It can be difficult for patients on the MAD to get enough fat to remain in ketosis, so sometimes dietitians will recommend supplementing with KetoCal® to increase daily fat intake. A 2010 study found that consuming one serving of KetoCal daily may help to improve the efficacy of the modified Atkins diet. - Supplements
Although the modified Atkins diet is less restrictive than the classic ketogenic diet, nutritional supplements are usually still required to ensure your child is meeting 100% of nutrition needs. Work with your dietitian to determine what, if any, supplements are necessary.
All versions of the ketogenic diet can be deficient in vitamins and minerals, including Vitamin D, the B vitamins and calcium, to name a few. This is one of many reasons why it is so important to only use the ketogenic diet and MAD under close medical supervision.
When is the modified Atkins diet Used?
- Steppingstone
Families might use the modified Atkins diet in preparation for starting the classic diet or as a trial to see if dietary management is likely to be helpful. - Transition
Some patients may follow the modified Atkins diet when transitioning off the classic ketogenic diet. Some health care providers and families prefer to wean gradually from the classic ketogenic diet, so they may switch to a MAD before discontinuing. - Time & Resource Limitations
Some families may not be able to commit to the requirements of initiating and managing the classic ketogenic diet, so the outpatient initiation and less restrictive nature of the modified Atkins diet may be more appropriate. - Older children, teenagers, and adults
Older children, teenagers, and adults may have trouble complying with the more restrictive classic ketogenic diet, so the modified Atkins diet may be easier for them to maintain.
If you are considering dietary management of epilepsy for help with seizure reduction, you will work with your doctor and dietitian to determine whether the classic ketogenic diet, modified Atkins diet, or another variation works best for you and your family.
KetoCal® is a medical food for the dietary management of drug-resistant epilepsy and is intended for use under medical supervision. Talk to your healthcare provider to determine if KetoCal is right for you.
Brought to you by Nutricia North America. Always consult with your ketogenic clinician prior to making any changes to your ketogenic diet or condition management. ©Nutricia North America 2025

